Moving to Australia is a dream for many, which is indicated by the number of visa applicants. In 2022, that number was 314,388 which was an increase from previous years.
What is particularly interesting is to see the number of individuals who are interested in moving from the United States to Australia. 818,000 Americans visited it in 2019.
That is why we think it is worthy to discuss this subject in greater detail.

Applying for an Australian Visa

With over 20 work-related visa options available, finding the right Australian visa is a pivotal part of the immigration process. The choice of visa depends on an individual’s employment situation, with some visas requiring nomination by an Australian employer.
The Australian government’s website provides comprehensive information on each visa type, including requirements and application procedures, ensuring prospective immigrants can find the visa most suited to their circumstances.
Here are the most common types of visas[1]:
| Visa Category | Visa Subclass(es) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Employer Sponsored Visa | 482, 186, 407, 494, 191, 457 | For those sponsored by Australian employers. |
| Skilled Visa | 189, 190, 489, 485, 476, 491 | For skilled workers based on qualifications. |
| Parent Visa | 870, 143, 173, 103, 804, 864, 884 | For parents of Australian citizens/residents. |
| Partner Visa | 461, 820 & 801, 309 & 100, 300 | For partners of Australian citizens/residents. |
Securing Employment in Australia
The first thing that an individual needs to do is to have a good reason for immigrating to Australia. There are two main ones, work and study.
Securing Work
Securing employment in Australia is a crucial step for many immigrants. The Australian government’s Priority Migration Skilled Occupation List[1.1] highlights in-demand occupations, facilitating the immigration process for individuals with specific skills.
For many work visas, applicants must be under 45 years of age, but exemptions exist for certain jobs on the list, offering flexibility for skilled professionals. The Australian government offers an array of over 30 visa options, including visas for skilled workers, working holidaymakers, and investors.
For those seeking to work in Australia, sponsorship can significantly enhance the chances of visa approval. Sponsorship opportunities can be pursued independently or through the Australian government’s SkillSelect program, which connects Australian employers with potential employees from around the world.
It’s important to note that the job search process in Australia can last up to several months, influenced by factors such as the specific industry, location, and current labor market conditions, according to the CICA report[2] .
Education

The procedure remains relatively the same when it comes to those interested in studying in Australia. The same goes for US citizens. According to the US embassy[3], nearly 12,000 are studying in Australia every year.
This is only a drop in the ocean because there were 725,000 foreign students in the country[4] in 2022, according to Times Higher Education.
A good indicator of how committed Australia is to providing education to foreign students is how many of them study in the country.
According to Statista[5]:
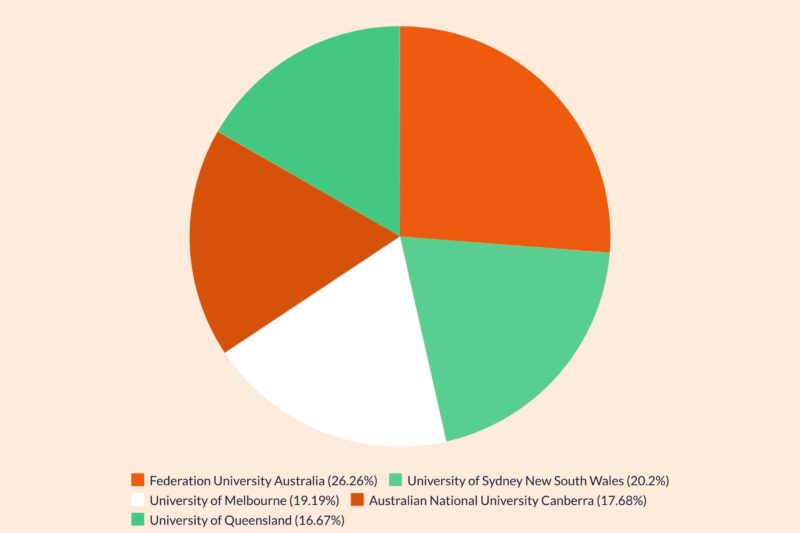
Popular Study Locations
Among the various Australian states, New South Wales and Queensland have emerged as the preferred destinations for US students. These regions are home to some of Australia’s most prestigious universities and offer a warm climate and cities like Sydney and Brisbane.
Visa Classification and Scholarships
American students benefit from being classified at Assessment Level 1[6] for student visas in Australia, which simplifies the application process and makes it more straightforward for them to obtain the necessary authorization to study. There are numerous scholarships available to US students wishing to pursue their studies in Australia.
The Endeavour Awards offer significant financial support, aiming to bolster international education links between Australia and the rest of the world.
Funding Opportunities
Understanding the financial aspect of studying abroad is crucial, and US citizens may be eligible to apply for student loans to fund their studies in Australia. Stafford loans and PLUS loans are among the options available, allowing students to finance their education and living expenses while abroad.
These are instrumental in making international education accessible to more students, ensuring that financial barriers do not hinder their academic and cultural experiences.
Preparing for the Move

Relocating to Australia from the USA is a significant undertaking that requires thorough preparation, not only in terms of logistics but also in ensuring compliance with health and legal requirements. A crucial aspect of this preparation is securing private health insurance.
Given the limited access to Australia’s public healthcare system for non-citizens, private health insurance is not just recommended but often mandated for immigrants, especially those on working and student visas.
This step is vital for ensuring that you have access to healthcare services[1.3] upon your arrival and throughout your stay in Australia. Organizing the logistics of moving your belongings is another critical step. Engaging an international moving company can greatly simplify this process.
Moving companies offer services that include secure packing, insurance, and tracking of your belongings, ensuring they are transported safely and efficiently to your new home. This service is invaluable for minimizing the stress and complications associated with international relocation.
Moving Options and Costs
When it comes to moving your possessions, you have two primary options:
- sea freight
- air freight
Sea freight is more affordable and can accommodate larger volumes, but it takes significantly longer, with shipments usually taking one to two months to arrive in Australia.
Air freight is faster, typically taking between five to eight days, but it is also more expensive and suitable for smaller volumes of belongings.
The choice between air and sea freight will depend on your specific needs, including how quickly you need your belongings and how much you’re moving. For those moving a household’s worth of items, sea freight is often the more practical choice, offering options for shared or exclusive containers to suit different volumes and budgets.
Settling in Australia

The cost of living in Australia, particularly in major cities like Sydney and Melbourne, is higher than in many other countries.
In fact, Australia is more expensive than 87% of countries[7] in the world.
The situation was pretty much the same even a decade ago when the country was officially the fourth most expensive country[8] in the world.
Despite these costs, Australia’s outdoor and family-focused culture facilitates easy assimilation for newcomers.
Living Expenses
For those planning to call Australia home, it’s essential to budget wisely. According to MasterPortal[9], living expenses in most Australian capital cities can range from $1,400 to $2,200 per month, excluding rent. These figures highlight the importance of financial planning for potential immigrants and expatriates.
When it comes to the rent, the situation looks like this, according to ABC News Australia[10]:
- Sydney – $745
- Canberra – $651
- Perth – $630
- Brisbane – $627
- Darwin – $611
- Melbourne – $565
- Adelaide – $565
- Hobart – $535
The rental market in Australia has seen fluctuations, influenced by border closures, COVID-19 lockdowns, and a decrease in international arrivals. These changes have impacted the availability and pricing of rental properties, making it crucial for newcomers to stay informed about the current market trends.
Permanent Residency and Citizenship

For those seeking long-term stay or retirement in Australia, pursuing permanent residency or citizenship is a viable path. Various visa schemes offer pathways to permanent residency, including employer-sponsored, skilled migration, and family visas.
Once permanent residency is established, immigrants can enjoy the benefits of living, working, and studying in Australia without restriction, with the option to apply for citizenship after meeting residency and other criteria.
There are three primary ways[11] to become an Australian citizen:
- By Birth: Individuals born in Australia to at least one parent who is an Australian citizen or permanent resident at the time of their birth automatically acquire citizenship.
- By Descent: Those born overseas to an Australian citizen parent are eligible for citizenship by descent.
- By Conferral: This common pathway is for permanent visa holders residing in Australia, encompassing those who have lived in the country for a specific period, demonstrating commitment to the Australian way of life and values.
Requirements for Citizenship by Conferral
The citizenship by conferral process is designed for permanent residents who have made Australia their home. Key requirements include:
- Being an Australian permanent resident
- Residing in Australia for four years, with at least one year as a permanent resident
- Demonstrating good character and an understanding of the responsibilities and privileges of Australian citizenship
- Intending to reside in Australia or maintain a close and continuing association with the country
- Special considerations and discretions may apply, such as for individuals born in Australia, partners of Australian citizens living overseas, and those with specific visas or skills beneficial to Australia.
Applying for Australian Citizenship
The application process for Australian citizenship involves submitting a completed application form, accompanied by the required documents and applicable fees, to the Department of Home Affairs (DOHA).
Applicants typically undergo an interview and must pass a citizenship test assessing their knowledge of Australia’s history, society, and the responsibilities and privileges of citizenship. Successful applicants are invited to participate in a citizenship ceremony, where they make the Australian Citizenship Pledge[1.3], officially marking their new status as Australian citizens.
References:
- 1. immi.homeaffairs.gov.au – Visa Options
- 1.1 immi.homeaffairs.gov.au – Visa processing times
- 1.2 immi.homeaffairs.gov.au – Health undertaking
- 1.3 immi.homeaffairs.gov.au – Australian Citizenship Ceremonies Code
- 2. CICA – Australian Job Report 2022
- 3. usa.embassy.gov.au – International education and research
- 4. timeshighereducation.com – Australia Emerges as the Most Popular Study Abroad Destination
- 5. statista.com – Share of international university students in Australia from 2023
- 6. hotcoursesabroad.com – Australian student visa
- 7. expatistan.com – Cost of living in Australia
- 8. theguardian.com – Australia is the fourth most expensive country in the world
- 9. mastersportal.com – Study Abroad in Australia: Tuition Fees and Living Costs
- 10. abc.net.au – a capital city breakdown of the most affordable suburbs
- 11. india.embassy.gov.au – Australian Citizenship
My name is Callum Anderson and I’m a freelance journalist and travel enthusiast who visited more than 50 countries in the last 10 years. My experience in obtaining documents for visiting different countries is immeasurable and I would like share it with as many people as possible.
Related Posts:
- Moving to Australia from the UK: A Beginner's Guide
- Why People Move to Australia: 10 Reasons Behind Relocation
- What to Know Before You Move From England to Scotland
- Work Culture in Australia: 13 Things What Americans…
- Visa Options for Americans Moving to Australia -…
- Top Job Opportunities in Australia for Expats





